Z-Matrix
A Z-matrix specifies molecular geometry relative to other atoms using bond lengths, bond angles, and dihedral angles.
While Z-matrices are a very intuitive coordinate system for chemists, they can occasionally cause numerical complications. Z-matrices are not unique (the same geometry can be specified by different Z-matrices), the geometry can be highly sensitive or insensitive to the underlying coordinates (e.g., rings or nearly linear systems), and sometimes they are ill-defined (e.g., a dihedral angle including three linear atoms).
WebMO creates a Z-matrix every time atoms are added or deleted. It is sometimes necessary to edit the default Z-matrix to specify a particular coordinate for scanning or to minimize numerical sensitivity in an optimization. The WebMO Z-matrix editor allows complete control over the Z-matrix for the current molecule.
The Z-matrix editor is invoked with Tools:Edit Z-Matrix...
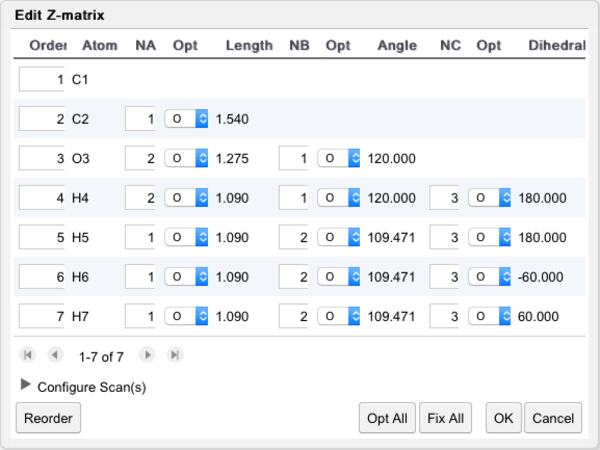
Z-Matrix Editor Dialog Box
Editing the Z-Matrix
When the Z-matrix editor is invoked, the index of each atom is displayed in the editor, and the View tool is activated. This is useful for visualizing the index associated with each atom, which is used in specifying the Z-matrix.
In the Z-matrix editor, the atoms are listed by element and atom index under the Atom column. The Z-Matrix entry for each atom is defined by the length, angle, and dihedral with respect to previously defined atoms under the Na/Length, Nb/Angle, and Nc/Dihedral angles, respectively. The Opt columns specify whether each coordinate is to be optimized (O), fixed (F), or scanned (S, S2).
Use the following procedure to edit the Z-matrix:
- Re-order the atoms if necessary. Simply change the numbering in the Order column on the far left, and click the ReOrder button. The atoms will be resorted in numerical order. The connectivity definitions will also change. (Note: Decimal and negative numbers are permitted to facilitate inserting atoms between other atoms.)
- Edit the connectivity definitions (Na, Nb, and Nc). Change the number(s) in the appropriate column. The lengths, angles, and dihedrals will be re-calculated. Note that you can only use previously referenced atoms in your definition.
- Mark coordinates to be optimized (O), fixed (F), or scanned (S, S2) if desired. Use the drop-down box next to each coordinate. Scan details are specified at the bottom of the editor.
If an atom is added or deleted, a new default Z-matrix is generated, and previous Z-matrix edits are discarded.
Atoms can only reference previously defined atoms in a Z-matrix. Thus, first re-order the atoms. Then define coordinates in terms of atoms ABOVE them in the Z-matrix.
Fixing Coordinates During a Geometry Optimization
Normally all coordinates optimized during a geometry optimization calculation. However, there may be instances where one desires to hold some coordinates fixed while optimizing the other coordinates, eg, to speed up the calculation, to optimize the geometry in successive stages, or because some aspects are defined by other constraints.
The Z-matrix Editor allows Z-matrix coordinates to be either optimized (O) or fixed (F) during a geometry optimization calculation. Since there are more internal coordinates (bond lengths, angles, and dihedrals) than Z-matrix coordinates, one may need to edit the Z-matrix to insure that the relevant coordinates are defined in the Z-matrix.
Specifying Coordinates to be Scanned
One can only scan a coordinate (bond length, bond angle, dihedral angle) that appears in the Z-matrix. Since Z-matrices are not unique, the coordinate to be scanned might not appear in the WebMO-generated Z-matrix. If necessary, re-order and/or re-connect the atoms in the Z-matrix so that the coordinate(s) to be scanned appear in the Z-matrix.
Specify that Start value, Stop value, and number of Steps for the scanned coordinate. Note that # Steps represents the number of points in addition to the first point, e.g., 10 steps will result in 11 calculations which include both the start and stop value.
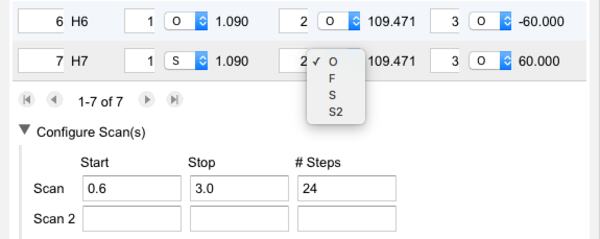
Specifying a Coordinate Scan
Optimizing or Fixing Other Coordinates During a Scan
Coordinates that are not scanned may be either optimized (O) or fixed (F) at each step. Clicking the Opt All or Fix All button prior to specifying the scan coordinates allows one to perform a "relaxed" scan or "rigid" scan, respectively. Optimizing all other coordinates requires significantly more compute time than fixing all other coordinates. It is also possible to keep some coordinates fixed while the remaining coordinates are optimized.
A coordinate scan can be defined without invoking the Z-matrix editor by selecting 2, 3, or 4 atoms, choosing Adjust:Scan Coordinate, specifying the scan details, and whether all the other coordinates are to be optimized ("relaxed scan") or fixed ("rigid scan"). The atoms are re-ordered and re-connected automatically by WebMO!
Dummy Atoms
Dummy atoms (X) may be inserted using the WebMO 3-D Editor. Dummy atoms are necessary for specifying an angle of 180 degrees, which is not generally supported in a Z-matrix definition. They are also useful for enforcing symmetry and thereby reducing the number of independent variables. When optimizing or scanning a molecule with dummy atoms, it is important to specify that the optimization be done using Z-matrix coordinates rather than redundant internal coordinates using Optimization Mode on the Advanced Job Options tab.