Coordinate Scan Calculations
A coordinate scan is the calculation of molecular energy as function of a geometric coordinate (bond length, bond angle, or dihedral angle). Sometime this is called a potential energy curve.
WebMO allows one to set up and run coordinate scan calculations by specifying the coordinate(s) to be scanned and whether the non-scanned coordinates are to be optimized or fixed.
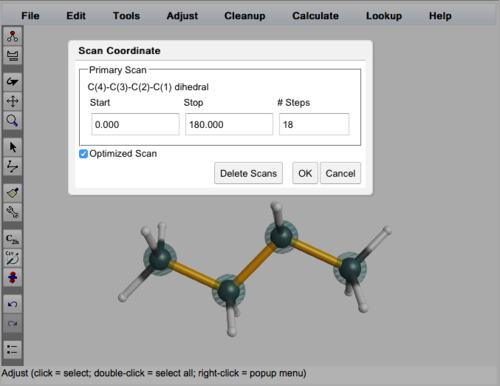
Scan Coordinate Dialog Box
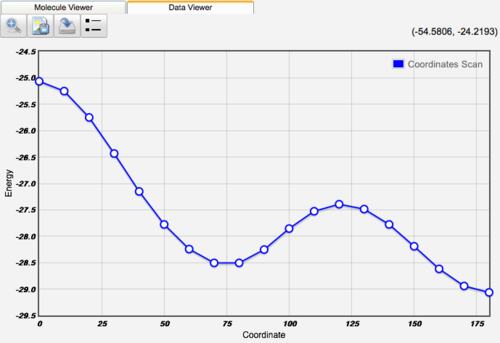
Butane Coordinate Scan
Coordinates to be Scanned
Any geometric coordinate (bond length, bond angle, dihedral angle) can be scanned. Using the adjust tool, select the 2, 3, or 4 atoms defining the bond length, bond angle, or dihedral angle to be scanned. Choose Adjust:Scan Coordinate. Specify that Start value, Stop value, and number of Steps for the scanned coordinate. Note that # Steps represents the number of points in addition to the first point, i.e., N steps will result in N+1 calculations which include both the start and stop value. Click OK.
The coordinate to be scanned will be indicated with gold bonds in the WebMO Editor.
To delete a scan coordinate, select atoms to define a scan, choose Adjust:Scan Coordinate, and click the Delete Scans button.
Type of Coordinate Scan
Coordinates that are not scanned may be either optimized or fixed depending on the choice of scan Type. Check Optimized Scan to optimize all coordinates at each step (except for the scanned coordinate, which is fixed as specified by the scan). This is sometimes called a "relaxed scan," as all non-scanned coordinates are allowed to relax energetically at each scan point. Leave Optimized Scan uncecked to fix all coordinates at each step. This is sometimes called a "rigid scan", as all non-scanned coordinates are fixed to their initial values.
A relaxed scan will require significantly more compute time than a rigid scan. Although both scan types have the same number of points, a relaxed scan performs a geometry optimization (except for the scanned coordinate) at each point, whereas a rigid scan performs an energy calculation at each point.
Running Coordinate Scans
Once the coordinate scan job has been defined, click the forward arrow ( ) on the bottom right to continue to the Choose Computational Engine page, and choose a computational engine supporting coordinate scans. Click the forward arrow to continue to the Configure Job Options page. The Calculation Type will automatically by selected as Coordinate Scan. Set any other desired job options, and click the forward arrow to run the job and return to the Job Manager page.
) on the bottom right to continue to the Choose Computational Engine page, and choose a computational engine supporting coordinate scans. Click the forward arrow to continue to the Configure Job Options page. The Calculation Type will automatically by selected as Coordinate Scan. Set any other desired job options, and click the forward arrow to run the job and return to the Job Manager page.
Two-Dimensional Coordinate Scans
A second coordinate can be independently scanned by defining another scan coordinate. It will appear with green bonds in the WebMO Editor. Note that taking N steps in the first coordinate and M steps in the second coordinate will require (N+1)x(M+1) points to be calculated.
Visualizing Coordinate Scans
1-D coordinate scans are plotted as energy vs. coordinate curves. 2-D coordinate scans are plotted as color coded countour maps. Results can be exported for subsequent analysis. See Visualizing Coordinate Scans for details.
Using the Z-Matrix Editor
While most coordinate scans can be setup automatically, the Z-Matrix Editor allows one to inspect how the coordinate scan will be setup and/or manually setup a coordinate scan. Z-matrices are not unique, and some will work better than others for a particular optimization or scan.
It is also possible to optimize some some non-scanned coordinates while the remaining coordinates are fixed, ie, a partially relaxed scan. Choose Tools:Edit Z-Matrix... to invoke the Z-Matrix Editor, and indicate which coordinates are to be optimized (O) or fixed (F).